Cables in Water Filled Pipes
This feature provides the capability to model cables deployed within water-filled pipes according to the guidelines outlined in IEC 60287-2-1.
Feature
The water inside the pipe is modelled as a solid body, with an assigned thermal resistivity calculated according to IEC 60287-2-1. The representation of this resistivity accounts for convective heat transfer. As a result, in the model, heat dissipates from the cable to its surroundings solely through conduction. The thermal resistivity is expressed as:
ρ = (2 * π * U)/(1+ 0.1 * De * ((V+(Y * θ) * ln(Dd/De))))
ρ = thermal resistivity applied to the pipe filling.
θ = the average temperature of water.
Dd = inner diameter of the pipe
De = diameter of the cable or an equivalent diameter of the group of the group of cable calculated according to IEC.
U = 0.1 (for water)
V = 0.03 (for water)
Y = 0.001 (for water)
For empty water filled pipes and water filled pipes without a heat source, a fixed thermal resistivity of 1.6 mK/W is applied.
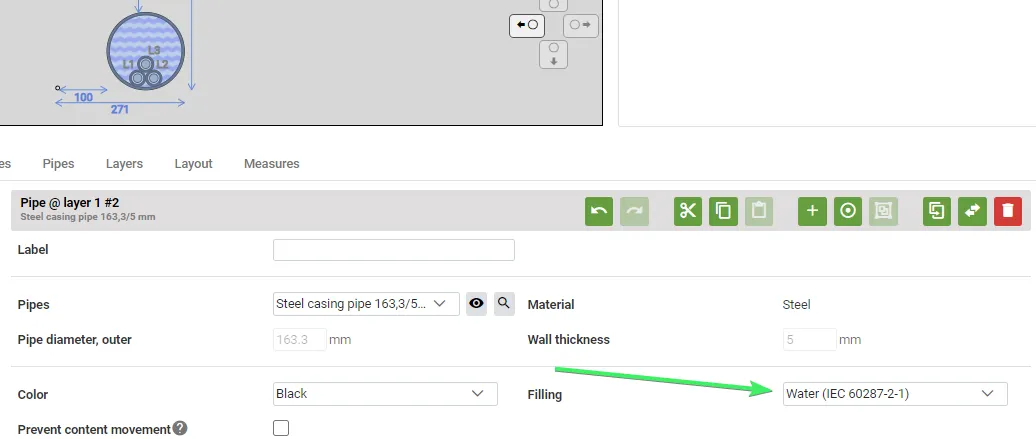
Applying the Feature in Grøft
To use this feature change the filling of a pipe from the default “air” to “water (IEC 60287-2-1)”
Limitations
This feature is applicable to all water-filled pipes but has the following limitations, which primarily affect the accuracy of the results.